Introduction to Online Security
In today’s digital age, the importance of online security cannot be overstated. As more individuals and businesses conduct their transactions online, the risks associated with weak passwords and inadequate protective measures have escalated significantly. According to recent studies, cyberattacks are increasingly common, with hackers constantly seeking vulnerabilities within online accounts. These threats underscore the necessity of employing robust security practices to protect one’s personal and financial information.
Weak passwords serve as an open invitation to cybercriminals. Many users tend to create passwords that are easy to remember but unfortunately also easy to guess. Passwords that include simple phrases, sequential numbers, or demographic information such as birthdays can be compromised with relative ease. Research indicates that nearly 81% of data breaches occur due to compromised passwords, highlighting the dire need for stronger security measures.
Furthermore, the rising sophistication of cyberattacks, including phishing schemes and brute-force attacks, complicates the landscape of online security. As technology evolves, hackers are developing more advanced methods to bypass even the most basic levels of account protection. Therefore, relying solely on a single-password system can no longer be considered sufficient in ensuring the safety of sensitive personal data.
To mitigate these risks, it is essential to adopt multi-faceted security strategies, including the use of strong passwords combined with two-factor authentication (2FA). Implementing such measures significantly enhances the security of online accounts, providing an additional layer of defense against unauthorized access. Securing accounts through these means is not only paramount for personal safety but also vital for preserving financial security in an increasingly interconnected world.
Understanding Password Vulnerabilities
In today’s digital landscape, password vulnerabilities pose significant risks to online security. One of the most prevalent issues is the reuse of passwords across multiple accounts. Users often opt to use the same password for convenience, but this practice can lead to catastrophic breaches. If one account is compromised, hackers can gain access to other accounts sharing the same password, making it imperative to create unique passwords for each service.
Another critical vulnerability is password predictability. Many individuals choose easily guessable passwords such as “123456” or birthdays, leaving their accounts exposed to brute force attacks. This phenomenon highlights the importance of selecting complex passwords that incorporate a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. A password that appears random and is longer than 12 characters significantly reduces the chances of successful hacking attempts.
Length plays a crucial role in enhancing password security. Research suggests that longer passwords are typically more secure. By increasing password length and complexity, users can create barriers that make it more arduous for attackers to decipher their credentials. Therefore, utilizing passphrases—a sequence of random words strung together—can serve as an effective strategy. Not only are they easier to remember, but they also allow for greater flexibility in terms of complexity.
The consequences of falling victim to password-related attacks can be severe, ranging from identity theft to financial loss. The impact of such breaches emphasizes the critical necessity of implementing robust password practices. By understanding these vulnerabilities and taking preventive measures, individuals can significantly enhance their online security and reduce the risk of unauthorized access to their accounts.
What is Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)?
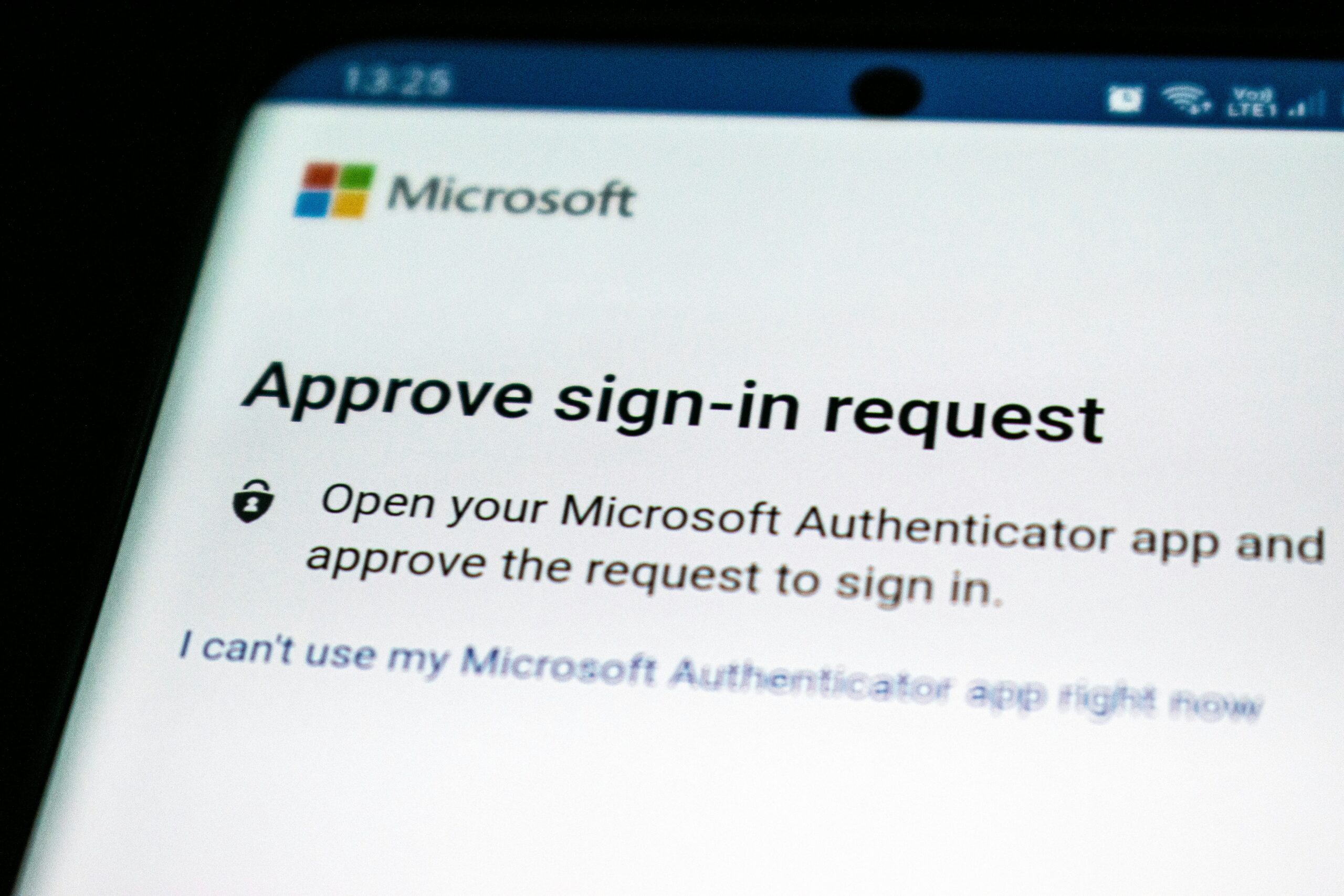
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) is a security measure designed to enhance the protection of online accounts by requiring two distinct forms of identification before granting access. This additional layer of security works in tandem with traditional username and password combinations, which have become increasingly vulnerable to unauthorized access due to various cyber threats such as phishing attacks and data breaches. By implementing 2FA, users significantly reduce the likelihood of their accounts being compromised.
The core principle of two-factor authentication lies in its requirement for two different verification methods. Typically, these methods fall into three categories: something you know (like a password), something you have (such as a smartphone app or a hardware token), and something you are (like biometric information). When logging into an account, users first enter their password, which represents the first factor. Subsequently, they must provide a second piece of information, often a code sent to their mobile device or generated by an authentication app. This process ensures that even if a password is intercepted, an attacker would still require the second form of authentication to gain access.
The importance of 2FA in safeguarding personal information cannot be overstated. Given the rise in cybercrimes, having this security measure in place acts as a critical deterrent against unauthorized access. A significant benefit of two-factor authentication is its ability to protect sensitive data and transactions, especially in an era where online banking and shopping are prevalent. By adding this extra layer of security, users can maintain greater control over their accounts and better protect their private information from malicious actors.
Types of Two-Factor Authentication
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is an essential security measure that significantly enhances the protection of online accounts. There are various methods for implementing 2FA, with each offering unique advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these options can help users choose the most suitable form for their needs.
One of the most commonly used methods is SMS-based verification. This approach involves sending a one-time code to the user’s registered mobile number whenever a login attempt is made. The primary advantage of SMS codes lies in their widespread accessibility, as most individuals possess a mobile phone. However, this method is not without its shortcomings; SMS messages can be intercepted by hackers through techniques such as SIM swapping, making this approach less secure than others.
Authenticator apps represent another popular form of two-factor authentication. These apps generate time-based one-time passwords (TOTPs) that users must input alongside their regular login credentials. A significant benefit of authenticator apps is their increased security, as they function independently of cellular networks and are not prone to interception. However, users must ensure they have access to their devices, as losing the device may complicate the recovery process.
For individuals seeking an even higher level of security, hardware tokens are an excellent option. These physical devices generate unique codes that users enter during the authentication process. Hardware tokens are highly secure, as they are not susceptible to remote attacks or password theft. Nonetheless, the reliance on a physical device may pose challenges if it is lost, stolen, or damaged, leading to potential access issues.
In summary, understanding the various types of two-factor authentication is crucial in selecting the best method for securing online accounts. Each method, whether it be SMS, an authenticator app, or a hardware token, comes with its own set of advantages and challenges. Users should evaluate their needs and circumstances carefully before deciding on the most suitable 2FA method for enhancing their account security.
How to Enable Two-Factor Authentication
Enabling two-factor authentication (2FA) is a vital step in safeguarding your online accounts. This security measure adds an extra layer of protection beyond just a password. Here, we provide step-by-step instructions on how to activate 2FA across popular platforms, including Google, Facebook, and various banking applications.
To begin, let’s focus on Google. First, log into your Google account and navigate to the “Security” tab located in the left sidebar. Here, you will find a section titled “Signing in to Google.” Click on “2-Step Verification” to start the setup process. You will be prompted to enter your password again for verification. Once authenticated, follow the on-screen instructions to choose your preferred second step, which can be a text message code, an authentication app, or a security key. Make your selection, and then follow any additional prompts to complete the setup.
Next, for Facebook users, go to your account settings by clicking the downward arrow in the upper right corner of your profile. Select “Settings & Privacy” followed by “Settings.” In the left menu, click “Security and Login.” Look for the option titled “Use two-factor authentication” and click “Edit.” You will have the option to receive a code via SMS or through an authentication app. Choose your preferred method, follow the prompts, and verify your setup.
For banking applications, the process may vary by institution. Generally, you will need to log into your account via the app or website, then navigate to the security settings section. Look for an option to enable 2FA and follow the on-screen instructions, which usually involve receiving a verification code via SMS or email to complete the activation.
By enabling 2FA on these platforms and keeping step-wise track of the process, you significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access to your accounts. This proactive approach to online security is highly recommended.
Creating Strong Passwords
In today’s digital landscape, creating strong passwords is a fundamental step in securing your online accounts. A robust password significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access. To establish an effective password, the first guideline is to focus on length; ideally, a password should contain a minimum of 12 characters. Longer passwords enhance security because they exponentially increase the number of combinations required to crack them.
Complexity is another important characteristic of a strong password. Incorporating a mix of uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters can thwart many common hacking techniques. For example, instead of using a simple passphrase like “Password123,” a more secure option would be “P@ssw0rd!2023.” This approach introduces unpredictability, making it considerably harder for malicious actors to guess or use automated tools to crack the password.
It is essential to avoid common pitfalls when creating a password. Many users tend to use easily guessable information, such as names, birthdays, or common words. Passwords like “123456” or “qwerty” are among the most frequently used, yet they offer little to no security. Consequently, combining unrelated words or utilizing passphrases can create a more secure option while still being memorable. For instance, consider a phrase like “PurpleElephant@Dawn,” which combines unrelated words and characters, enhancing both security and memorability.
Additionally, it is advisable to utilize different passwords for each of your accounts. Reusing passwords increases vulnerability because if one account is compromised, others become susceptible as well. To manage numerous passwords effectively, consider employing a password manager. These tools generate, retrieve, and store complex passwords securely, allowing users to focus on remembering only one master password while ensuring robust security across various online platforms.
Using Password Managers
Password managers are essential tools that facilitate the management of your online credentials, enhancing security while minimizing the risks associated with password reuse. These applications store and encrypt your passwords, allowing you to create unique and complex passwords for different accounts without the burden of memorizing each one. By employing a password manager, individuals can generate strong passwords that are difficult to decipher, significantly reducing the likelihood of unauthorized access to their accounts.
One of the key benefits of utilizing a password manager is its ability to streamline the login process. Instead of needing to remember every password, users can access their accounts securely with a single master password. The password manager will then autofill the required fields, saving valuable time while ensuring high security. Moreover, most password managers integrate two-factor authentication, adding an additional layer of protection to your accounts.
When selecting a password manager, it is crucial to consider several factors. First, ensure that the tool employs strong encryption standards, such as AES-256, to protect your stored data. Additionally, look for features like secure password sharing, two-factor authentication support, and cross-platform compatibility, which ensures that your credentials are accessible across different devices. User-friendliness is also significant; an intuitive interface can greatly enhance your experience, making it easier to manage your passwords effectively.
There are numerous password management tools available, both free and premium. Well-known options include LastPass, Dashlane, and Bitwarden, each offering diverse features to meet varying security needs. Ultimately, choosing a reliable password manager not only enhances your account security but also simplifies the process of maintaining robust and complex passwords across your online accounts.
The Importance of Unique Passwords
In the digital age, the importance of unique passwords cannot be overstated. With the increasing number of online services that require users to create accounts, it has become common practice to reuse passwords across multiple platforms. However, this approach poses significant risks to personal and sensitive information. When users opt for the convenience of using the same password, they inadvertently present a larger target for cybercriminals. If one account suffers a data breach, hackers can exploit this to gain access to other accounts where the same password is utilized.
Unique passwords serve as robust barriers against unauthorized access. By ensuring that each online account is protected by a distinct passphrase, a user can effectively mitigate the risk of widespread compromise. If one password is discovered, the attacker is limited in their ability to infiltrate other accounts protected by different passwords. This segmentation is a crucial aspect of maintaining strong online security. Furthermore, using unique passwords encourages the adoption of complex password habits, which can be further enhanced by employing a mix of uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
Employing unique passwords also simplifies the management of login credentials, especially when paired with a reputable password manager. These tools can securely generate, store, and autofill unique passwords, making it easier for users to adhere to security best practices without the burden of memorization. In a landscape where cyber threats are ever-evolving, the strategy of using unique passwords for each account is not merely advisable; it is essential for safeguarding personal data and ensuring a secure online experience. Prioritizing unique passwords can significantly bolster the effectiveness of overall account security measures, setting a strong foundation for safe internet use.
Recognizing Phishing Attempts
Phishing attacks are deceptive tactics used by cybercriminals to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information, such as passwords and personal details. These attacks can take various forms, often imitating legitimate organizations to gain the trust of unsuspecting targets. The primary goal of phishing is to obtain confidential information that can be exploited for malicious purposes.
One common method employed by attackers is email phishing, where fraudulent messages appear to be from reputable sources, such as banks or online services. These emails often urge recipients to click on links or download attachments that lead to fake websites resembling legitimate login portals. Here, users may unwittingly enter their credentials, providing attackers with direct access to their accounts. It is crucial to scrutinize email addresses closely, as minor alterations can indicate a potential scam.
Social media platforms also become fertile ground for phishing attacks. Cybercriminals craft messages or posts that appear to come from friends or well-known figures, enticing users to click on malicious links. Additionally, some attackers engage in spear phishing—a targeted approach where specific individuals are targeted through personalized messages based on gathered personal data. Recognizing these tactics is essential in fortifying one’s defenses against such schemes.
To mitigate the risk of falling victim to phishing attempts, it is imperative to adopt several preventive measures. Always verify the authenticity of any communication that prompts you to provide personal information. Avoid clicking on links or downloading attachments from unknown sources. Implementing tools such as email filters and ensuring that your device has up-to-date security software can provide an additional layer of protection. By remaining vigilant and informed about the strategies employed by attackers, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of being victimized by phishing scams.
Regularly Updating Passwords
Regularly updating passwords is an essential practice for maintaining the security of online accounts. With the increasing frequency of data breaches, it is crucial to ensure that access credentials remain robust and unyielding against potential cyber threats. The primary aim of password updates is to reduce the risk of unauthorized access, especially after a breach has been reported concerning a particular service or platform. Even if you have not received any alerts regarding security incidents, adopting a routine for changing passwords can bolster your defense against evolving cyber threats.
To manage password changes effectively, consider establishing a schedule for updates. A recommended best practice is to change passwords every three to six months. This timetable helps in reducing the chances of an old or compromised password being exploited. Moreover, when changing a password, it is advisable to avoid using easily guessable information such as birthdates, names, or sequential characters. Instead, aim to create complex passwords that are unique for each account, ideally incorporating a mix of uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
In the context of managing multiple passwords across various accounts, utilizing a password manager can simplify the task while enhancing security. These tools can generate strong, random passwords and securely store them, thus making it feasible to change passwords regularly without the burden of memorization. Furthermore, after a data breach, it is critical to change passwords for affected accounts immediately, and consider enabling two-factor authentication as an added layer of protection.
In conclusion, regularly updating passwords is a vital component of online security. By adhering to best practices and leveraging tools such as password managers, individuals can significantly enhance the safety of their accounts and protect themselves from potential security breaches.
Account Recovery Options
As cyber threats continue to evolve, securing online accounts is of paramount importance. A crucial aspect of maintaining the integrity of an account, especially when two-factor authentication (2FA) is enabled, is understanding the various recovery options available. This double barrier, while effective against unauthorized access, can sometimes hinder legitimate users from recovering their accounts. Therefore, it is essential to familiarize oneself with account recovery methods to ensure that access can be regained seamlessly.
One common recovery option involves the use of backup codes. When setting up 2FA, most platforms offer users a set of one-time backup codes that can be printed or stored securely. These codes serve as a safety net, allowing access in scenarios where the primary authentication method (such as a mobile device) is unavailable. Users should ensure these codes are stored in a safe location, separate from the device used for 2FA, to prevent unauthorized access.
Another method is to establish an alternative verification method. Many platforms allow users to associate secondary email addresses or phone numbers with their accounts. This secondary contact can be utilized to send verification links or codes to facilitate account recovery. When configuring these alternative methods, it is imperative to choose contacts that are secure and not easily compromised.
Additionally, some services offer the option of security questions that can be utilized for account recovery. While this feature can provide an extra layer of security, users should choose questions that are difficult for potential attackers to answer. This proactive approach enhances both security and recoverability.
Ultimately, being proactive about account recovery options is essential for securing online accounts. Ensuring multiple recovery methods are set, understood, and easily accessible can help users regain access swiftly in the event of a lockout, thereby maintaining the security of their online persona.
Social Engineering Attacks
Social engineering attacks represent a significant threat to the security of online accounts, even in the presence of robust protective measures such as strong passwords and two-factor authentication (2FA). These attacks exploit human psychology rather than technical vulnerabilities, allowing attackers to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data by manipulating individuals. The various tactics employed in social engineering attacks include phishing emails, pretexting, baiting, and tailgating, each designed to trick the target into divulging confidential information.
Phishing, for instance, often involves crafted emails that appear legitimate, prompting users to click on malicious links or provide personal information on fake login pages. Attackers can bypass even strong passwords by simply asking the victim for their login credentials, luring them into a false sense of security. Furthermore, in the case of pretexting, an attacker creates a fabricated scenario to establish trust and convince the victim to share their private information, potentially undermining the effectiveness of 2FA.
To mitigate the risks associated with social engineering attacks, individuals and organizations must enhance their awareness and develop effective countermeasures. One crucial strategy involves educating users about the signs of potential social engineering attempts. This can include awareness campaigns that detail the characteristics of suspicious emails or phone calls, as well as training on how to recognize phishing tactics. Additionally, adopting a cautious approach when sharing sensitive information, even with familiar contacts, can significantly reduce the likelihood of falling victim to these manipulative techniques.
Further efforts can involve implementing robust security policies, such as verifying requests for sensitive data through alternative channels before responding. By establishing a culture of skepticism and continual vigilance, users can significantly strengthen their defenses against social engineering attacks. Ultimately, protecting online accounts requires a combination of technological safeguards and heightened awareness of the human element inherent in cybersecurity threats.
The Role of Security Questions
Security questions have long been an integral part of the user authentication process, intended to add an extra layer of protection to online accounts. These questions often revolve around personal information, such as the name of a childhood pet or the city where one was born, making them seemingly helpful in verifying identity. However, the effectiveness of security questions is increasingly being called into question. Many users may choose answers that can be easily guessed or discovered through social media profiles, thereby compromising the intended security.
Moreover, as individuals become more aware of privacy implications, they may find themselves uncomfortable sharing certain information. This discomfort can lead to vague responses, further diminishing the reliability of security questions. Research has shown that many commonly used security questions can be easily answered through public records or social media scrutiny. This inherent vulnerability raises significant concerns about the robustness of this particular security measure.
Instead of relying solely on security questions, it is advisable to implement more secure alternatives. For example, users can utilize password managers that generate strong, unique passwords for each of their accounts, thus minimizing the chance of unauthorized access due to weak passwords. Additionally, two-factor authentication (2FA) significantly enhances security by requiring a second form of identification, such as a code sent to a mobile device. This multi-layered approach to security is more reliable than security questions, which only serve as a singular point of verification.
In conclusion, while security questions were once considered a reliable method for account protection, their limitations have made them less effective. Users are encouraged to embrace stronger security practices, such as using unique passwords and enabling two-factor authentication, to truly secure their online accounts.
Secure Your Devices
In the modern digital landscape, securing your devices is paramount to ensuring the safety of your online accounts. Laptops, smartphones, and tablets serve as gateways to personal information, making them prime targets for cybercriminals. Protecting these devices should be a priority for any user who values their online security. A multi-faceted approach is essential, starting with the installation of reputable antivirus software. This type of software serves as the first line of defense against malware, viruses, and other malicious software that could compromise your sensitive information. It is advisable to keep this software up-to-date so that it can effectively counter evolving threats.
In addition to antivirus protection, enabling device encryption is another critical step in securing your devices. Encryption transforms your data into unreadable code, making it inaccessible to unauthorized users. Most operating systems provide built-in encryption tools, such as BitLocker for Windows devices and FileVault for macOS, which can help safeguard your data in the event of theft or loss. For smartphones, both Android and iOS offer encryption options that should be activated. This added layer of security ensures that even if someone gains physical access to your device, the data remains unreadable without the correct passcode or biometric authentication.
Regular software updates are also fundamental to device security. Operating system and application updates often include patches that protect against known vulnerabilities. Users should enable automatic updates when available, ensuring they are protected from the latest security threats. Furthermore, employing strong passwords that differ across accounts can complement these security measures effectively. Together, these strategies can significantly enhance the security of your devices, ultimately protecting your online accounts and providing peace of mind in an increasingly interconnected world.
Monitoring Account Activity
Regularly monitoring your account activity is a crucial aspect of online security. With the increasing prevalence of cyberattacks, vigilance becomes paramount. By keeping an eye on your account activity, you can identify any unfamiliar logins or suspicious behavior that could indicate a security breach. Most online services provide a way to view recent activity, allowing you to see details such as login timestamps, locations, and device information.
To effectively monitor your accounts, start by logging into your various online accounts and navigating to the security settings. Look for options like “Recent Activity” or “Login History.” Many platforms will list all recent logins and may highlight any attempts from unknown locations or unusual devices. It is advisable to note down your typical login patterns so that you can easily spot any irregularities.
If you receive alerts of an unfamiliar login, or if you see any activity that seems out of the ordinary, act swiftly. Most platforms allow you to log out of other sessions remotely. Take this step immediately if you suspect unauthorized access. Subsequently, change your password to something stronger and unique, integrating strong password practices that enhance security further.
In addition, enabling notifications for account activity can add an extra layer of protection. Many services allow you to receive email or text alerts whenever there is a login from a new device or location. This creates an immediate avenue to address any suspicious activity quickly. Staying proactive and informed about your account activity will help ensure your online accounts remain secure, ultimately protecting your sensitive information from potential threats.
Educating Others About Online Security
Online security is a critical aspect of maintaining digital safety, and it is essential to share knowledge with friends and family. Many individuals may not fully understand the risks associated with weak passwords and the absence of two-factor authentication (2FA). By informing others about the significance of securing their online accounts, we can collectively build a more secure online environment.
First, it’s imperative to explain the concept of strong passwords. A strong password typically combines a mixture of uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. It should be at least 12 characters long to enhance security. When discussing passwords, emphasize the necessity of unique passwords for each account, as using the same password across multiple platforms increases vulnerability. Password management tools can further assist individuals in maintaining strong, unique passwords without the difficulty of memorizing them all.
In tandem with educating about password strength, introducing the concept of two-factor authentication is equally important. 2FA adds an extra layer of security by requiring an additional form of identification beyond just the password. This secondary verification, which may involve a text message code or an authentication app, drastically decreases the likelihood of unauthorized access. Encouraging friends and family to activate 2FA on their accounts not only protects their personal information but also minimizes potential risks presented by data breaches.
Moreover, fostering discussions about online security can lead to a more informed community. Organizing informal gatherings or digital workshops where individuals can learn about best practices for securing their online accounts can be immensely beneficial. Providing resources, sharing articles, and offering assistance can enhance awareness and motivate others to prioritize online security. By collaborating in this manner, we can ensure greater safety for all in our increasingly connected world.
Future of Online Security
The landscape of online security is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and the increasing sophistication of cyber threats. As digital interactions continue to rise, the necessity for robust security measures, including two-factor authentication (2FA) and strong passwords, becomes more imperative than ever. Emerging trends indicate that authentication technologies are embracing multi-layered security protocols that extend beyond traditional passwords.
One significant advancement is the rise of biometric authentication methods. These techniques utilize unique biological identifiers such as fingerprints, facial recognition, and iris scans to verify a user’s identity. As these technologies mature, they offer enhanced security and user convenience, reducing the reliance on easily compromised passwords. Moreover, behavioral biometrics, which analyze patterns in user behavior, are gaining traction, providing an additional layer of protection against unauthorized access.
The advent of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) has also reshaped the field of online security. These technologies help in identifying anomalies and potential security breaches in real-time. By scrutinizing user behavior and recognizing deviations, AI systems can alert users to suspicious activities promptly. This proactive approach allows for immediate responses to threats, ultimately improving the overall security posture of users.
Despite these advancements, several challenges persist. One key issue is user complacency regarding strong passwords and 2FA adoption. Many individuals still favor convenience over security, which leaves them vulnerable to cyberattacks. Moreover, the continuous evolution of cyber threats necessitates staying abreast of new security technologies and practices. Cybercriminals are constantly adapting their strategies, making it essential for users to prioritize their online security.
In conclusion, the future of online security pivots towards more advanced technologies and user-focused strategies. The implementation of biometric solutions, coupled with AI and ML advancements, holds the potential to greatly enhance account security, provided users remain engaged and proactive in their security practices.
Resources for Further Learning
In an era where online security is of utmost importance, it is crucial to remain informed about best practices for protecting personal information. A variety of resources are available to deepen one’s understanding of two-factor authentication (2FA) and password management, ensuring that individuals can navigate the complexities of digital security effectively. Below are some valuable platforms and materials to consider.
For those seeking foundational knowledge, the website of the Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) offers extensive resources on online safety. Their guides cover essential topics such as creating strong passwords and implementing 2FA in various applications. Additionally, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) provides comprehensive documents and recommendations for secure password practices.
Online learning platforms like Coursera and edX feature courses that delve into cybersecurity fundamentals, including password management strategies and the importance of 2FA. Enrolling in such courses enables participants to grasp core concepts and acquire actionable skills for their cybersecurity toolkit. Furthermore, websites like Khan Academy present informative videos that can simplify complex topics related to digital safety.
Additionally, engaging with articles from reputable tech publications, such as Wired or Ars Technica, can provide deeper insights into recent developments in online security. These articles often discuss the latest trends and best practices in safeguarding accounts, including the implementation of diverse authentication methods.
Lastly, community forums like Stack Exchange and Reddit offer platforms for individuals seeking advice or sharing personal experiences related to online security. Participating in these discussions can foster learning and help users stay updated on potential threats and effective countermeasures.
By utilizing these resources, individuals can cultivate a robust understanding of two-factor authentication, strong password practices, and overall online security, making informed choices to protect their digital identities.
Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Online Security
In today’s digital age, safeguarding your online accounts has become more critical than ever. The combination of strong passwords and two-factor authentication (2FA) serves as a robust shield against unauthorized access. As we have discussed, strong passwords should be complex, unique, and regularly updated. This foundational step is vital because many breaches occur due to easily guessable passwords or the reuse of passwords across multiple sites.
Two-factor authentication further enhances security by adding another layer of protection. By requiring a second form of identification, such as a code sent to your mobile device, 2FA significantly reduces the risk of account breaches, even if your password is compromised. The integration of these two security measures creates a formidable barrier against cyber threats.
Moreover, being proactive in managing your online security settings is essential. Regularly reviewing account activity for suspicious behavior can lead to early detection of potential threats. Enabling alerts for unusual sign-ins is another preventive measure that all users should consider. Additionally, utilizing password managers can help maintain unique passwords for each account, simplifying password management while ensuring enhanced security.
Ultimately, taking control of your online security is not just a recommendation; it is a necessity in our hyper-connected world. By adopting strong passwords and enabling two-factor authentication, you empower yourself to mitigate risks significantly. Encourage others to take these steps as well, because a collective effort in online security considerably decreases the likelihood of cyberattacks. Empower yourself and others today to foster a safer online environment for everyone.